ABO / Rh Incompatible Stem Cell Transplant (NHSBT 2011)
Intro
30,000 HSCT performed in Europe in 2012
30-50% are ABO-mismatched
BMT Journal 2015 – UK study - ABO mismatch does not affect OS in RIC HSCT
background
ABO incompatibility does not affect graft rejection or GVHD since ABO antigens are not expressed on primitive stem cells --> large numbers of ABO incompatible transplants because HLA type trumps ABO in donor selection.
Maximum haemolysis usually occurs 9-16 days post-transplant, occasionally severe and intravascular.
More common with PBSC than bone marrow due to a higher number of lymphocytes being infused.
Very rare if graft has been T-cell depleted with alemtuzumab, or undergone CD34+ cell selection.
Complications of ABO incompat HSCT
Pure red cell aplasia
Haemolysis – 4-5% of all HSCT. Risk increased by unrelated donors and chronic GVHD.
Passenger lymphocytes – unexpected antibodies produced by lymphocytes transplanted into patient. Usually occurs 7-10 days post-transplant. Self-limiting until lymphocytes die. DAT+. IgG usually but can be IgM.
Definitions
Major ABO incompatibility
Presence in the recipient’s plasma of Anti-A, Anti-B or Anti-A,B antibodies incompatible with donor red cells, e.g. Group A donor, Group O recipient
Potential Risks
Acute haemolysis at time of stem cell infusion
Delayed haemolysis due to production of antibodies by residual host lymphocytes
Minor ABO incompatibility
Presence in the donor’s serum of Anti-A, Anti-B or Anti-A,B antibodies reactive with the recipient’s red cells, e.g. Group O donor, Group A recipient
Potential Risks
Acute haemolysis at time of stem cell infusion due to Anti-A or Anti-B in the donor plasma product
Delayed haemolysis of recipient cells due to passenger lymphocyte syndrome
Bidirectional
The presence in both the donor and the recipient’s plasma of anti-A, anti-B or anti-A.B antibodies reactive with the recipient and donor cells respectively, e.g. Group A donor, Group B recipient
Risks as for both of the above
Investigations
Pre-transplant
ABO + D group and antibody screen
Anti-A and Anti-B titres by IAT
DAT
Post-transplant
Monitor for haemolysis – immediate and delayed
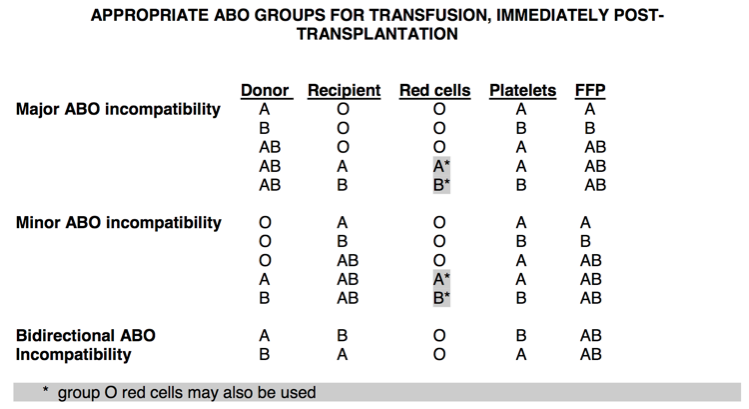
Choice of ABO group for transfusion
Pre-Transplant
Recipient type red cells and platelets should be given
Post-Transplant
Pre-engraftment
Major Incompatibility
Red Cells: Recipient ABO group, or group O
Plts/FFP: If the donor is group AB, use group A high titre negative units if the recipient is group A and use group B high titre negative units if the recipient is group B.
Minor Incompatibility
Red Cells: Donor ABO group
Plt/FFP: If the recipient is group AB, use group A high titre negative units if the donor is group A and use group B high titre negative units if the donor is group B
Bidirectional
Red Cells: Group O
Plt/FFP: AB plasma and recipient group platelets
Post-engraftment
This is defined as when all of the following criteria are met:
ABO antibodies to the donor group are undetectable in the reverse grouping and by IAT (applies to major incompatibility only)
The DAT is negative using polyspecific AHG
Conversion to donor group is complete, with no mixed field reactions (in practice this is only demonstrable once there have been no red cell transfusions for three months)
Graft Rejection
Following graft rejection use recipient group red cells and platelets.
Choice of Rh D group for transfusion
Pre-Transplant
Recipient type red cells and platelets
Post-Transplant
Major Incompatibility
RhD negative components until RhD positive cells are detected. Thereafter give RhD positive.
Minor Incompatibility
RhD negative components indefinitely.
N.B. Some hospitals use group O red cells indefinitely for all patients
Solid Organ Transplant
Renal Transplant
Historically ABO compatible only as kidneys express A&B antigens —> failed engraftment
Now using immunoabsorption to remove IgG Anti-A and Anti-B (live donations only)
Accommodation = process by which graft kidney persists post-transplant even once recipients anti-A or anti-B titre rises again
Liver Transplant
Need a lot of blood, already been sick for some time, may have had previous transplants
Often already have antibodies
Blood bank attends the liver transplant MDT to plan product supply
Beyond 10 units can drop antibody / ABO matching due to dilution and depletion of patient’s own plasma
When to ABO incompat liver transplants occur?
Error
Super emergency cases
Paediatrics
Rh D+ organ --> Rh D- recipient
1500 units Anti-D
Flow cytometry 48 hours later
Circulatory Death Donors
Can use normothermic ECMO with donor blood and blood products matched to donor
Provides regional circulation to the organ due to be harvested
Ex-Vivo Normothermic perfusion (EVNP)
Prior to transplant and during transport of organ around the country
Designed to improve the quality of marginal organs and so increase the donor pool
Group O used to perfuse the organ