oxidative haemolysis
Precipitants of oxidative haemolysis
Drugs
Dapsone, Co-trimoxazole, Rasburicase, Sulfasalazine, Antimalarials, Chloramphenicol, Methylene blue, Quinolones, Nitrofurantoin
(Aspirin, Quinine and Pencillin but not at conventional doses)
Food
Fava beans (contain oxidising agents divicine and isouramil)
Infection
Hep A, Hep B, CMV, Pneumonia & Typhoid are known triggers of haemolysis in G6PD deficient patients
Other acute illness
e.g. DKA
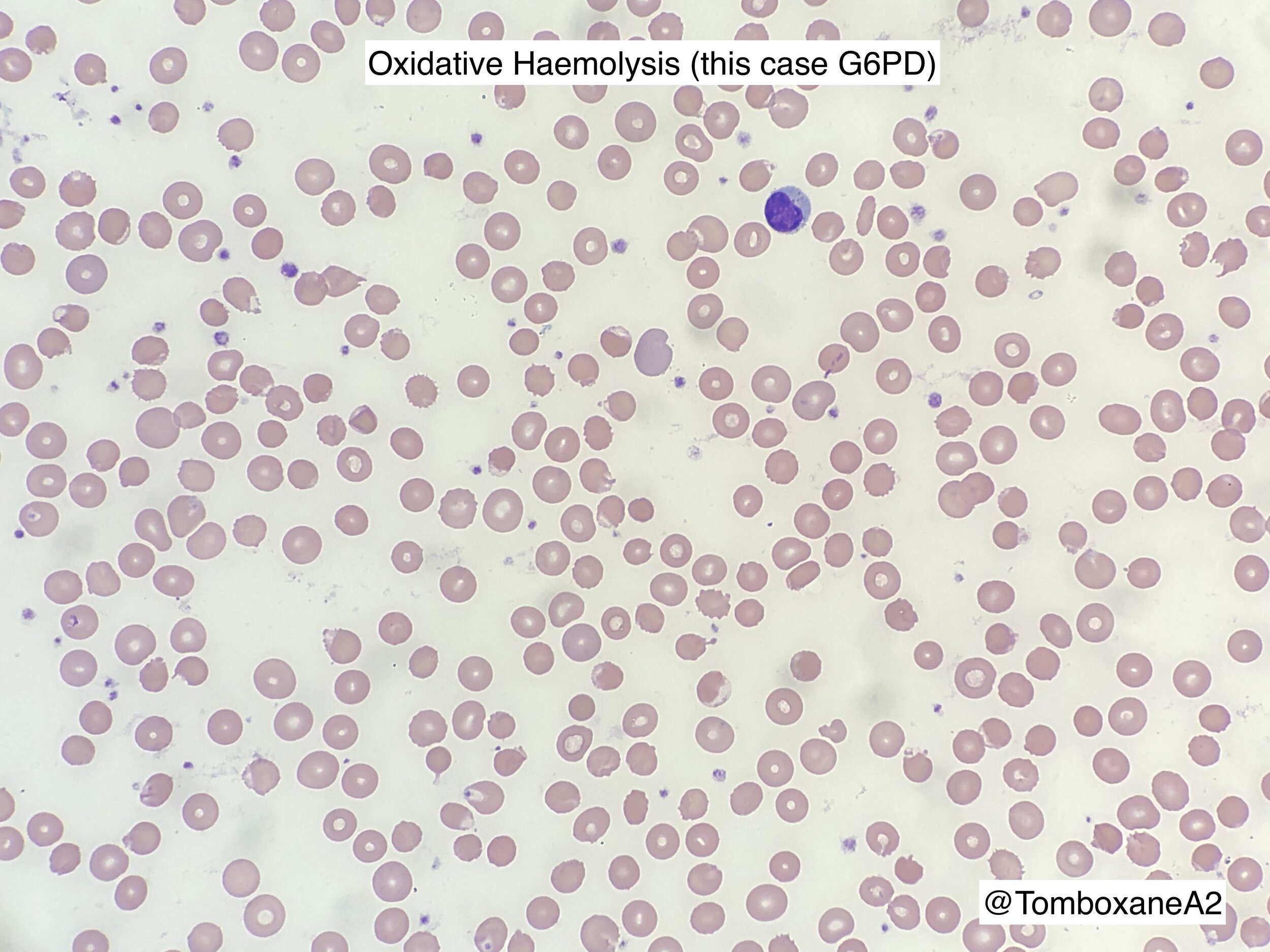
Blood film Morphology
G6PD Deficiency (BSH 2020)
Intro
X-linked
Female carriers have increased resistance to malaria
Variable phenotype, broadly:
Mild in Black Africans (termed ‘G6PD A-’)
Moderate in Asians
Severe in Mediterraneans
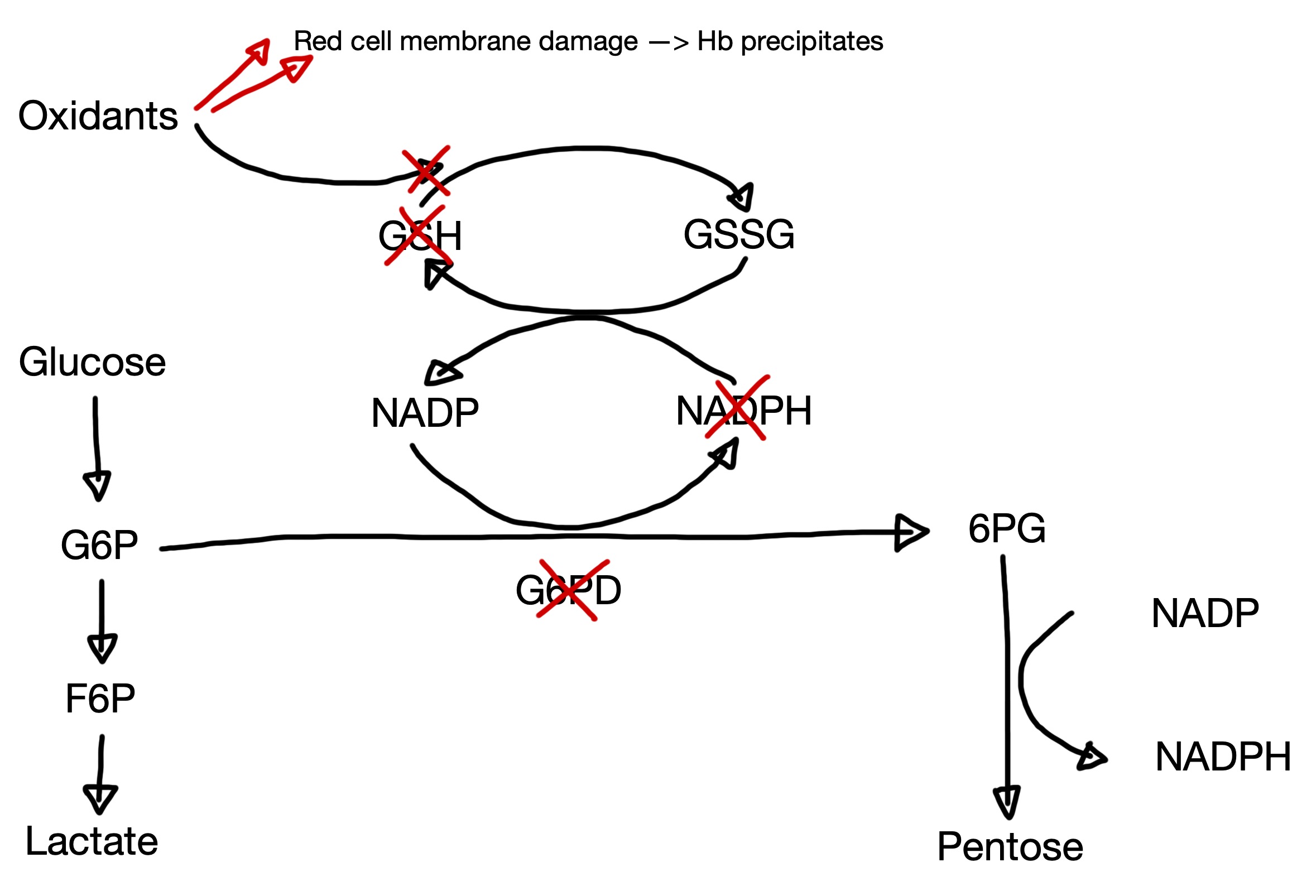
Pathophysiology
G6PD reduces nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADP) to NADPH
This is the only source of NADPH for the red cell
NADPH is needed to reduce glutathione
Reduced glutathione clears free oxidants --> deficiency results in increased susceptibility to oxidative stress.
Clinical Features
Neonatal Jaundice - peaks at 2-3 days after birth. Variable severity.
Acute Haemolysis - triggered by ‘oxidant’ drugs / food / infections (see top of page)
Chronic non-spherocytic haemolytic anaemia (CNSHA)
Laboratory Investigation
Principle of test - measurement of G6PD activity depends on detecting the rate of reduction of NADP to NADPH.
Qualitative screening tests for G6PD deficiency include:
Fluorescence spot
Dye decolourisation
Analytical variables affecting G6PD tests:
Reticulocytes have higher concentrations of G6PD, so tests performed after a recent haemolytic episode may produce false negatives
Anaemia and leukocytosis also interfere with screening tests
Recent red cell transfusion
A positive screening test should be followed by a quantitative assay
Women suspected of having G6PD deficiency should be tested by quantitative assay as the screening tests may produce false negatives.
Molecular testing by PCR or Sanger sequencing is available - potentially useful in recently transfused patients or heterozygous females.